Tax management refers to the management of finances, for the purpose of paying taxes. Tax Management deals with filing Returns in time, getting the accounts audited, deducting tax at source etc. Tax Management helps in avoiding payment of interest, penalty, prosecution.
Elements of tax management
1. Filing return.
2. Auditing
3. Source deduction
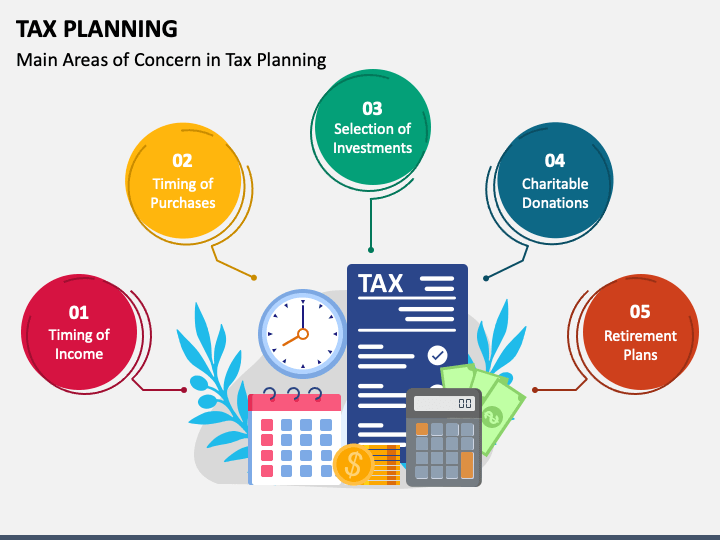
- To minimise litigation: To litigate is to resolve tax disputes with local, federal, state, or foreign tax authorities. There is often friction between tax collectors and taxpayers as the former attempts to extract the maximum amount possible while the latter desires to keep their tax liability to a minimum. Minimising litigation saves the taxpayer from legal liabilities.
- To reduce tax liabilities: Every taxpayer wishes to reduce their tax burden and save money for their future. You can reduce your payable tax by arranging your investments within the various benefits offered under the Income Tax Act, 1961. The Act offers many tax planning investment schemes that can significantly reduce your tax liability.
- To ensure economic stability: Taxpayers’ money is devoted to the betterment of the country. Effective tax planning and management provide a healthy inflow of white money that results in the sound progress of the economy. This benefits both the citizens and the economy.
- To leverage productivity: One of the core tax planning objectives is channelising funds from taxable sources to different income-generating plans. This ensures optimal utilisation of funds for productive causes.